Raman Spectroscopy is universally accepted as the most reliable and accurate analysis method for art works. It is valuable in the restoration of art works, but also for the determination of their authenticity.
Raman Spectroscopy is universally accepted as the most reliable and accurate analysis method for art works. It is valuable in the restoration of art works, but also for the determination of their authenticity.Its main advantage is that it is non - destructive as there is no need to remove samples from the object in question for analysis. In addition it can be applied in situ without transferring the object to some laboratory.
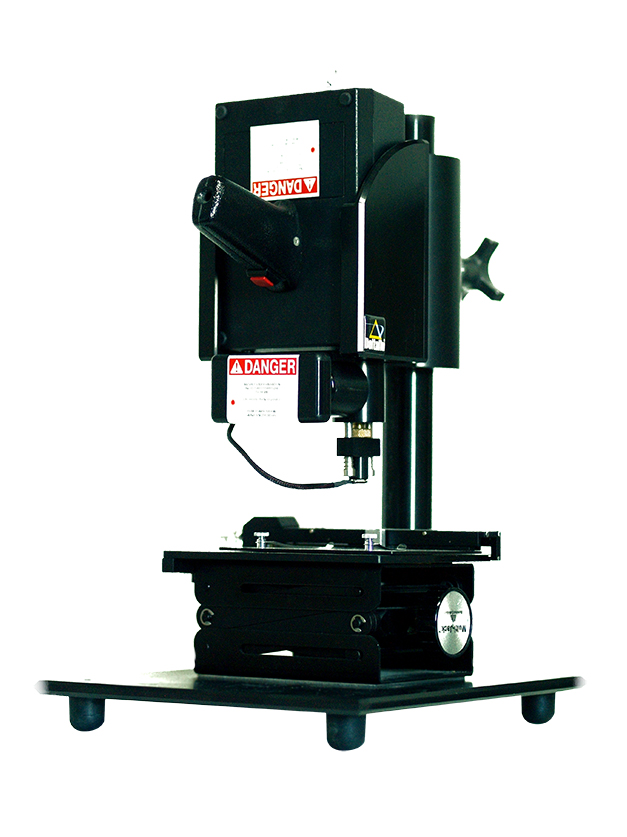

Raman Spectroscopy recognizes the molecular structure and the chemical composition of organic and inorganic materials, natural or synthetic. Since the Raman spectrum for every substance is unique, the identification of a specific substance is achieved by comparing its spectrum to spectra found in libraries that have been created and are available internationally in the form of databases.
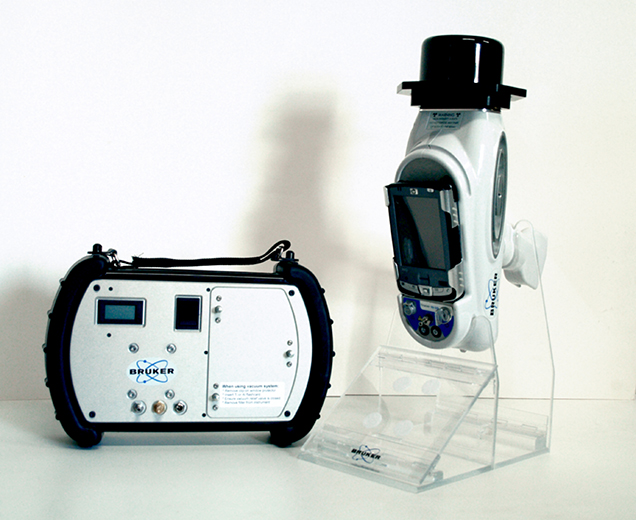
The NIKIAS Research Center owns and operates an advanced, transportable variable power Raman Spectroscope with a laser beam of 785nm. The Center has access to the databases in the international bibliography and also uses its own extended database on colors and materials that are available in the Greek market as well as those that have been used by contemporary and past Greek painters.
The up-to-date transportable system of Elemental XRF Analysis model Tracer III-SD manufactured by Bruker generates X-Rays Rh of a maximum of 40KV and can analyze light elements such as Mg, Al and SI. It provides the necessary scientific information for the analysis and identification of inorganic coloring substances and hence it is the most essential analytical instrument for the study, maintenance, and certification of authenticity of paintings and other art objects.It provides a non-destructive method for study and analysis which consists of making spectra readings on any point of the surface of paintings (in situ) and comparing them to prototype spectra from a fully populated database that has been developed.Besides the study of art objects, X-Ray Fluorescence is used ever increasingly in archaeometry as a basic non-destructive method for analyzing and certifying coloring substances.
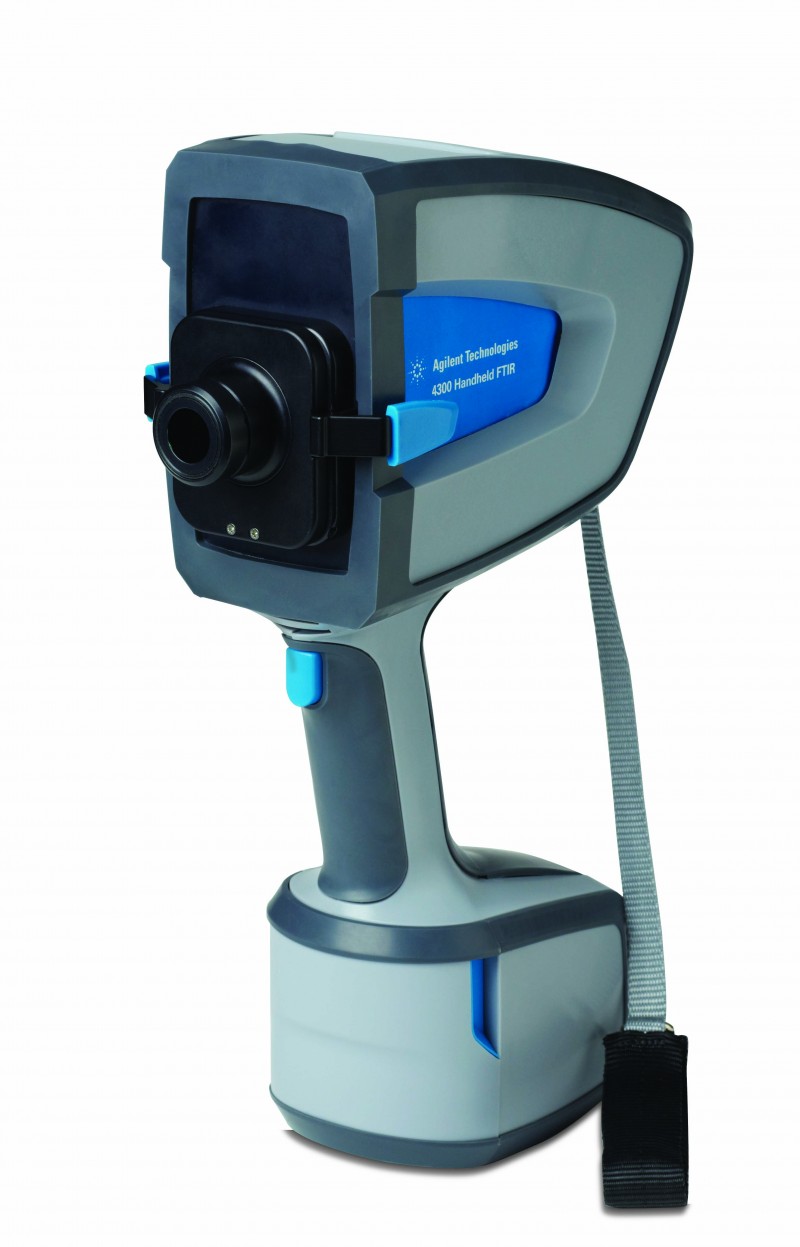 The recently acquired instrument for analysis via Infrared Spectroscopy is FTIR by Agilent Technologies. It is the first integrated analysis system for paintings and art objects of its kind in Greece. It provides the necessary scientific information for the identification of coloring substances via an absolutely non-destructive method of study and analysis with the use of state-of-the-art ATR ZnSe Probe with the DTGS Detector 045-5010 that facilitates the recording of spectrum readings from any point on the surface of a painting (in-situ).
The recently acquired instrument for analysis via Infrared Spectroscopy is FTIR by Agilent Technologies. It is the first integrated analysis system for paintings and art objects of its kind in Greece. It provides the necessary scientific information for the identification of coloring substances via an absolutely non-destructive method of study and analysis with the use of state-of-the-art ATR ZnSe Probe with the DTGS Detector 045-5010 that facilitates the recording of spectrum readings from any point on the surface of a painting (in-situ).In addition the Miracle ATR Single Refl. ZnSe accessory allows the recording of spectrum readings from controlled samples of coloring substances and hence it can be used for the creation of an integrated database of reference spectra.
Besides the study of art works, Infrared Spectroscopy is used as a fundamental analysis method in archaeometry. Its important advantages compared to other methods are the non-destructive in-situ analysis, the quick and easy operation of the equipment and the reliability of the results. For the best possible results this method is applied as a compliment to Raman Spectrography and X - Ray Fluorescence.
The complete test methodology applies to paintings while portions of the methodology are applicable to sculptures and other art objects made of ceramics, glass, wood, bone and fabric. The test methodology is always adjusted in order to take into account the special properties of the investigated objects while we continuously seek to employ more advanced procedures that increase the completeness of the analysis and certification of the objects that we examine.